Clinical
Development
Program
Tissue Repair recently concluded Phase IIB trials on its proprietary molecule, Glucoprime, which has yielded promising statistical data supporting the progression to Phase III trials.
- Overview
- Pivotal Clinical Studies
- Early Clinical Studies
- Pre Clinical Studies
- Phase III Clinical Pathway
Clinical Development
Program Overview
Tissue Repair recently concluded Phase IIB trials on its proprietary molecule, Glucoprime, which has yielded promising data supporting the progression to Phase III trials.
The randomised, double blinded and placebo-controlled Phase IIB chronic wound trial was completed in 2020 under FDA approved protocols and results show drug efficacy is comparable to the current therapies.
Phase III trials are planned to commence in 2024 to replicate the results of the Phase IIB trials with a larger trial cohort.
Successful Phase III trials and subsequent approval by the regulatory authorities will permit the product to be used to treat chronic wounds.
Over 240 patients across two indications have been studied across Phase I, Phase IIA and Phase IIB clinical studies with TR-987. Most studies (involving over 200 subjects) were randomised, double-blind and placebo-controlled. The majority of the study patients recruited have been in the USA under an Investigational New Drug (IND) Application, with the remainder having been recruited as part of studies undertaken in Australia.
Tissue Repair is in the final stages of completing its Phase II program, having recently completed Phase IIB clinical study data collection and statistical analysis across two indications: chronic wounds and aesthetic dermatology. The Company is planning to file end of study reports for its two Phase IIB trials with the FDA in 2021.
All Phase II trials have been undertaken employing FDA-approved protocols:
- Randomised: Trial subjects assigned to treatment or control groups using an element of chance to reduce selection and/or allocation bias.
- Double-blind: Neither the participants nor the administers know if they are being administered the placebo or trial treatment. Information which may influence the participants in the experiment is withheld.
- Placebo-controlled: Control group receive a non-effective “placebo” treatment specifically designed to have no real effect in order to benchmark again the treatment being trialled.
In a trial, patients can fall into two cohorts:
- Intention-To-Treat (ITT): Defined as patients that were randomised and recorded one observation. By way of example, if a patient withdrew in week 4 of a 12-week treatment period, they would still be included in the ITT group.
- Per Protocol (PP) or Completer Cohort: Defined as those patients that received the full course of treatment and the full dosage of TR-987, representing those patients that adhered to the approved trial protocol.
| Phase | Indication | Status | Year | Location | Patients | Design | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phase I/II | Chronic wounds (venous leg ulcers) | Completed | Australia | 6 | Open, observational |
|
|
| 18 | Double-blind, randomised, placebo controlled |
|
|||||
| Phase IIA | Chronic wounds (venous leg ulcers) | Completed | 2006 | Australia | 58 | Double-blind, randomised, placebo controlled |
|
| Phase IIA | Aesthetic (facial laser ablation) | Completed | 2007 | USA | Pilot – 12 Main – 26 |
Double-blind, randomised, placebo controlled |
|
| Phase IIB | Aesthetic (chest laser ablation) | Completed | 2020 | USA | 42 (across two studies with the same protocol) | Double-blind, randomised, placebo controlled (FDA approved) |
|
| Phase IIB | Chronic wounds (venous leg ulcers) | Completed | 2020 | USA/Australia | 82 | Double-blind, randomised, placebo controlled (FDA approved) |
|
Ablative fractionated lasers have been increasingly utilised in recent years to improve the appearance of UV-induced photo-damage, skin wrinkles (rhytides) and scarring. Postoperative skin care is critical in promoting optimal wound healing after therapy, however there is currently no gold standard post procedural product.
This study examined the efficacy of TR-987 in wound healing (epithelialisation) and improving skin quality following CO2 ablative laser treatment of the chest.
The trial, which was done at a single site in San Diego, USA, and was randomised, double-blind, and placebo-controlled. The trial initially involved 22 patients and was later extended to include a further 20 patients (under two protocols which were materially identical). The data from both studies (n=42) was pooled and analysed. Two patients were lost to follow up (one each from the active and placebo groups) and an Intention-To-Treat (ITT) analysis was done on 42 patients together with a Modified Intention-To-Treat (MITT) analysis on the 40 patients who completed the trial.
The validated 3- and 9-point Fitzpatrick-Goldman Wrinkle and Elastosis Scale (respectively) was used to evaluate the effectiveness of the TR-987 0.1% gel in promoting post-procedure healing most notably as it affected skin quality of the underlying procedure as compared to control. Both test and control regimens promoted safe and effective healing of the chest skin after the procedure.
Wrinkling
For the MITT group, 85% of responders achieved a wrinkling score of 1 or greater (i.e. 33% improvement) for the active group compared to the placebo group (where only 50% of responders achieved a wrinkling score of 1 or greater. The absolute difference of 35.0% is statistically significant (p = 0.041). The figure details the proportion of patients within each of the TR-987 and placebo groups who achieved a ≥1-point improvement in wrinkling scores between baseline and day 28 (Fitzpatrick-Goldman Classification).
Elastosis
For the MITT group, 75% of responders achieved an improvement score of 3 or greater in elastosis (i.e. 33% improvement) for the active group compared to the placebo group where only 35% of responders achieved the same level of improvement. The absolute difference of 40.0% is statistically significant (p = 0.011). The figure details the proportion of patients within each of the TR-987 and placebo groups who achieved a ≥3-point improvement in elastosis scores between baseline and day 28 (Fitzpatrick-Goldman Classification).
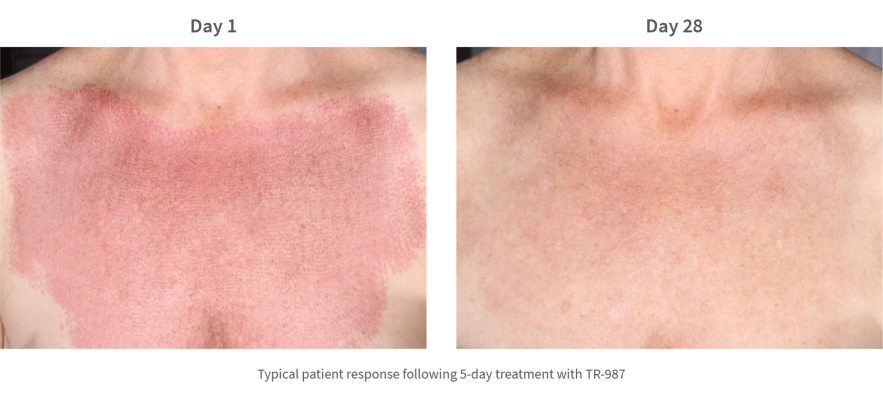
The study investigators confirmed TR-987 to be an efficacious topical treatment following laser ablation in regard to improving skin quality as measured by elastosis and wrinkling.
Chronic Wounds
Pivotal Clinical Studies: Phase IIA
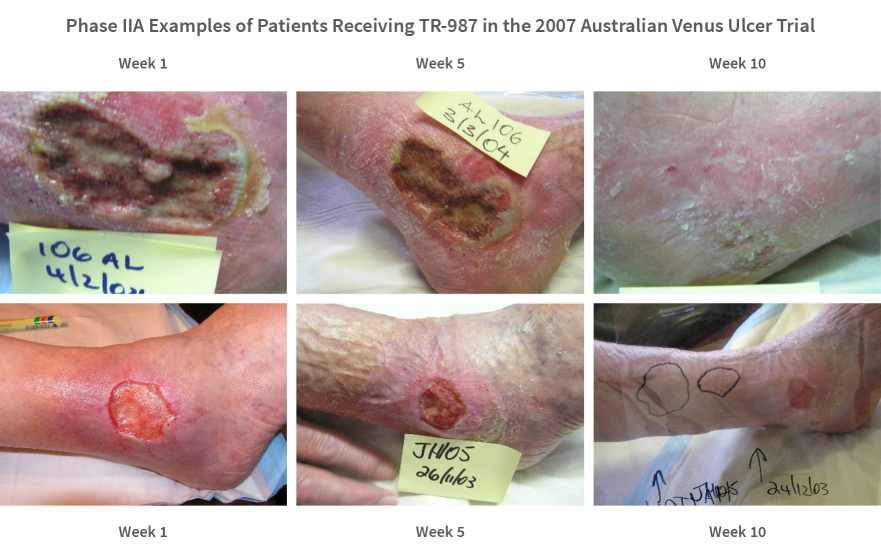
Phase IIA: Study of TR-987 (MG-36) in the Treatment of Chronic Venous Insufficiency Ulcers (MG3601, Australia, 2006).
The objectives of the study were to determine the efficacy of TR-987 in the promotion of repair of chronic venous insufficiency ulcers. The efficacy of two dosages of active ingredient, 0.1% and 1.0% GlucoprimeTM, were tested and assessed for safety and tolerance in ulcers of the lower limbs.
This was a 58 patient, Phase II, double-blind, placebo-controlled study with patients assigned to one of the three treatment groups on a randomised basis using a computer-generated allocation sequence. There were two active treatment arms (0.1% and 1.0% active ingredient respectively) in order to assess the dose-response effect of Glucoprime and a control arm of gel base with no active ingredient. The study was intended to provide a statistical assessment of the efficacy and safety of TR-987 in patients with chronic venous insufficiency ulcers of the leg. It was anticipated that the outcomes from this study would contribute towards the planning of a pivotal Phase III trial.
A subset of the Intention-To-Treat population, in which all subjects had measurements at both baseline and Day 85, was created and called the ‘Completer’ population for further analysis of efficacy (n = 14 in the high dose (1.0% TR-987) group and n = 15 in each of the low dose (0.1% TR-987) and placebo groups).
For the data analysis, non-parametric Wilcoxon rank sum tests with the Normal approximation were performed on the difference between placebo and each of the active treatment groups in the change in ulcer area from baseline to Day 85 for the Completer population. Statistically significant differences were found in the change in ulcer area from baseline to Day 85 for the high dose (1.0% TR-987) group compared with placebo (p = 0.022), and for the low dose (0.1% TR-987) group compared with placebo (p = 0.008).
Secondary analyses were carried out on the percent change from baseline to Day 85 for both populations using Wilcoxon ranked sum tests with the Normal approximation. There appeared to be a greater percent reduction in the low and high TR-987 dose groups than in placebo. While these apparent differences provided a positive indication of efficacy, they were not statistically significant, possibly due to the large variability in the data and to the relatively low sample sizes.
| Percent Change In Ulcer Area From Baseline | Intention-To-Treat Group (n=55) | Completer Group (n=44) (all subjects had measurements at both baseline and Day 85) |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Treatment | Median change in ulcer area | p-value | Median change in ulcer area | p-value |
| High Dose (1.0%) | -55.9% | 0.598 | -55.9% | 0.432 |
| Low Dose (0.1% | -59.0% | 0.301 | -66.7% | 0.115 |
| Placebo | -35.7% | -35.7% | ||
There was no evidence of any significant toxicity in any of the three treatment groups. Therefore, the safety profile for both the high and low dose formulations of TR-987 gel, as well as for the gel base, was considered to be acceptable.
Chronic Wounds Pivotal Clinical Studies: Phase IIB
Phase IIB: Study of the Efficacy of TR 987, beta-1,3-1,6-D-glucan, in the Treatment of Chronic Venous Insufficiency Ulcers (BG001, Australia/USA, 2020).
The objectives of this study were to assess the time to heal within 12 weeks between chronic VLUs treated with TR 987 gel and Standard of Care (SoC) versus placebo gel and SoC.
This study was an 82 patient, multi-centre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study to evaluate the effectiveness of TR-987 gel on venous leg ulcers. It included a two-arm design with one group having received twice-weekly applications of 0.1% TR-987 in a gel base plus standard of care (SoC) for the first 4 weeks. The other group received twice-weekly applications of placebo gel base plus SoC for the same period. After 4 weeks, both groups received once weekly applications of their assigned treatment for the remaining 8 weeks of the trial.
Preliminary analysis of the trial has been conducted by Tissue Repair, with the final study report expected to be lodged with the FDA in 2021.
Statistical analysis was undertaken on both Intention-To-Treat (n=67) and Per Protocol (n=49) cohorts for the intended indication range of 2-12cm² and indicated that the primary objective of time to heal showed no difference between any of the groups. A key secondary objective of proportion of wounds healed, however demonstrated a positive signal of efficacy which is notable given wound closure is considered the gold standard FDA endpoint for wound healing.
Key findings from the preliminary analysis include the following:
- 20.6% adjusted improvement* in incidence of complete closure (p=0.12) for the Intention-To-Treat Group (n=67) for 2-12 cm² ulcers (logistic regression analysis)
- 27.37% improvement in incidence of complete closure (p=0.1029) for the Per Protocol group (n-49) 2-12 cm² ulcers (logistic regression analysis)
- Almost double the percentage wound area reduction in chronic venous leg ulcers 90.5% TR-987 vs 46.6% placebo for the per protocol group (p=0.035); 2-12cm² ulcers
*Adjusted difference based on logistic regression analysis, controlling for factors known to affect healing
- TR-987 per protocol group from the Phase IIB trial are those patients that completed the trial and received the full drug dosage over the 12-week period
- Intention-To-Treat group includes all patients randomised including all withdrawals
- A clinically meaningful difference is generally considered to be +10% difference of absolute closure
- TR-987 achieved 20.6% adjusted difference in incidence of complete closure vs adjusted incidence of complete closure for the current standard of care of 17%. Meaningful differences for the Intention-To-Treat group and Per Protocol groups are recorded
- Adjusted data is based on logistic regression (TR-987) and Cox regression (current standard of care) controlling for factors known to affect healing between the groups (e.g. base line ulcer size)
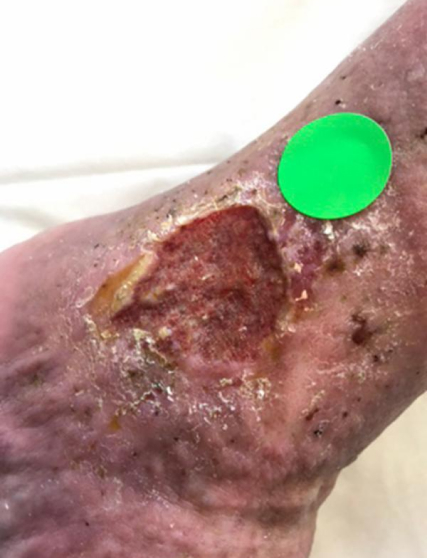
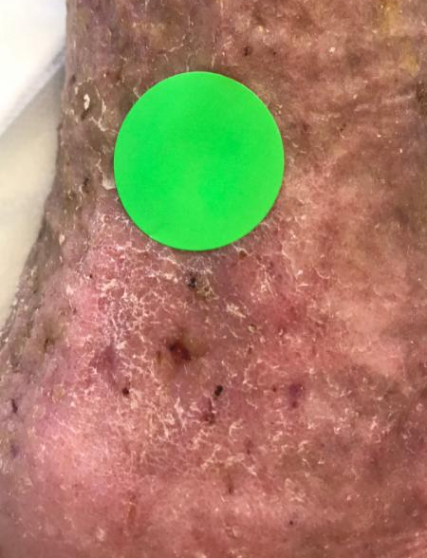
A typical example of a VLU wound healed with TR-987 2020 Phase IIB Venus Leg Ulcer trial n=67 (2-12cm²). 7.53cm² at screening (Heidelberg Repatriation Hospital Melbourne) Ulcer present for 208 weeks (4 years prior to enrolment) patient age was 72 with leg ulcers present from age 57
The ITT group includes all patients including early withdrawals while the PP group removes those patients who did not adhere to the protocol and were withdrawn prior to the 12-week treatment period and is considered a more meaningful measure of efficacy
NB: The protocol was undertaken during COVID-19 which caused a spike in patients lost to follow up. Ulcers were on average significantly larger in the Active group with 12 of the 36-patients having ulcers between 7-12 cm², This in comparison to placebo where only 2 of the 31 patients had ulcers in the 7-12cm² range.
The Phase IIB trial provided additional positive data in regard to the efficacy of TR-987 and confirmed a target indication wound size of 2-12cm² for the forthcoming Phase III trial.
When comparing the endpoint of average percentage of wound area reduction, the Phase IIB trial demonstrated a similar robust efficacy signal to the 2007 Phase IIA trial as shown below
- The 2007 Phase IIA trial treated severe wounds. Absolute mean wound area reduction (in mm²) showed statistically significant results between groups (p=0.08)
- 2007 phase IIA FDA VLU trial, mean percent wound area reduction for the completer group, low dose vs placebo. Note absolute mean wound area reduction showed statistically significant results [reduction of 1428mm² in low dose at day 85 vs 1084mm² in placebo (P=0.008)]
- 2020 Phase IIB FDA VLU trial mean percent wound area reduction for the 2-12cm² ulcer range per protocol group (the company’s target indication range
Phase I: Safety
Early Clinical Studies
Phase I: Study of the Safety of TR-987, beta-1,3-1,6-D-glucan, in the Treatment of Chronic Deep Venous Insufficiency (CDVI) Ulcers (Australia, 2007).
Glucoprime was studied in six patients with lower limb ulcers due to chronic deep venous insufficiency (CDVI) disease. Patients were selected on the basis of the long-standing nature of their ulcers and failure to respond satisfactorily to standard wound management. The test article was applied every 2-3 days for 4 weeks, and the ulcers were assessed weekly for response and signs of toxicity. The ulcer area was determined by planimetry.
No significant intolerances or toxicities were observed or reported in association with the use of the test article. A healing response was observed in all 6 patients, with an average reduction of 55% in wound surface area, measured over a 56-day period.
Phase I: Efficacy
Early Clinical Studies
Phase I: Study of the Efficacy of TR 987, β-1,3-1,6-D-glucan, in the Treatment of Chronic Deep Venous Insufficiency (CDVI) Ulcers (CTN 96108, Australia, 2007).
Phase I and II studies confirmed the ability of Glucoprime to stimulate and further initiate healing within chronic trophic ulcers.
The Phase IIA study sought to identify the optimal formulation (i.e. concentration of Glucoprime) of TR-987 gel that yielded the greatest efficacy.
Phase IIB was focused on further demonstrating the efficacy and safety of TR-987 against standard of care combined with a placebo gel.
The drug product has been well tolerated by patients across all clinical trials confirming a strong safety profile.
The completion of Phase II will be marked by an end of Phase II meeting with the FDA whereby Tissue Repair will share its findings from the Phase II patient trials and propose plans for a Phase III clinical study.
The efficacy of Glucoprime was studied in a single-centre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial in 18 patients with CDVI ulcers that had become refractory to standard wound management therapies. Glucoprime was compared to another form of glucan (Glucodine) with a lower molecular weight range and a smaller proportion of (1->6)-β-glucan side-branching, and to the placebo (control). Patients were randomly assigned to the three treatment groups (two active groups and one placebo control group), with 6 patients per group. Treatment was 3 times weekly for 4 weeks. No intolerances or toxicities were observed or reported in association with the use of either of the active test articles or placebo control. Efficacy was assessed by planimetry, measuring the surface area of the wound. The primary efficacy parameter was the improvement in ulcer surface area from baseline (visit 1) to the end of the trial (visit 6). The mean rates of improvement over 4 weeks were as indicated in the table. Ulcer healing was improved in patients in the Glucoprime group compared to placebo, and the results of this study were used to plan further studies using a larger number of patients over a longer treatment period.
| Summary Mean Rates Of Ulcer Improvement Over 4 Weeks | |
|---|---|
| Treatment | Percent Reduction In Wound Surface Area After 4 Weeks Of Treatment (a minus value indicates wound worsening) |
| Glucoprime (high molecular weight API) | 36.7% |
| Glucodine (low molecular weight API) | -17.3% |
| Placebo (control) | 4.4% |
Phase II: Safety & Efficacy
Early Clinical Studies
Phase II,: A Double-blind, Randomized, Placebo-controlled Study to Investigate the Safety and Efficacy of 0.1% and 1.0% Topically Applied GLYC-101, Compared to Placebo, in Patients Undergoing CO2 Laser Skin Resurfacing of the Lower Eyelids (GLYC-101-1b, USA, 2008).
The study evaluated the safety and efficacy of two concentrations of TR-987 (low and high Glucoprime dosages) compared to placebo (gel base), in promoting wound healing on the lower eyelid skin of 26 subjects undergoing fractionated CO2 laser skin resurfacing for cosmetic purposes (wrinkle reduction). Overall, when compared to placebo, treatment with TR-987 (high Glucoprime dosage) or TR-987 (low Glucoprime dosage) was safe and well tolerated.
The comparison of each TR-987 arm to placebo with respect to the primary endpoint (mean time to complete wound closure / epithelialisation) showed positive results when considering the full subject dataset from all treatment combinations. Specifically, the efficacy outcome of time to complete wound closure was 20-30% shorter for TR-987 at 1.0% and 0.1% (13.1 days and 10.9 days, respectively) compared to placebo (16.3 days; p = 0.0062 and 0.0331, respectively).
Pre Clinical Studies
In vivo studies looking at incisional wounds in mice, rats, guinea pigs and mini pigs have all confirmed clinical efficacy of Glucoprime (the Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient (API) of TR-987) and its precursors.
The primary effects of the Glucoprime therapy were enhanced migration of macrophages and neutrophils into the wound space, followed by earlier onset of all aspects of the healing cascade.
Leibovich SJ, Danon D. Promotion of wound repair in mice by application of glucan. J. Reticuloendothel. Soc. 27, 1-11 (1980)
Proposed Phase III
Clinical Pathway
Tissue Repair has commenced preparatory work for the TR-987 Phase III clinical trial on venous leg ulcers and is expecting the study to take an estimated 36 months to complete, assuming no delays in patient recruitment, or onerous FDA requests in relation to the characterisation of the active ingredient, Glucoprime.
The Phase III clinical trial is being designed in accordance with FDA requirements to allow Tissue Repair to pursue regulatory approval in the USA. If successful, TR-987 may be the only topical drug approved for wound care in the USA since 1997 and as such, may represent a valuable asset with a significant market opportunity.
The key work streams required to successfully commence, and complete Phase III trials include:
| A | Analytical development and product manufacture |
|
| B | Regulatory |
|
| C | Phase III trial |
|
Program Overview
Tissue Repair recently concluded Phase IIB trials on its proprietary molecule, Glucoprime, which has yielded promising data supporting the progression to Phase III trials.
The randomised, double blinded and placebo-controlled Phase IIB chronic wound trial was completed in 2020 under FDA approved protocols and results show drug efficacy is comparable to the current therapies.
Phase III trials are planned to commence in 2024 to replicate the results of the Phase IIB trials with a larger trial cohort.
Successful Phase III trials and subsequent approval by the regulatory authorities will permit the product to be used to treat chronic wounds.
Program Overview
Over 240 patients across two indications have been studied across Phase I, Phase IIA and Phase IIB clinical studies with TR-987. Most studies (involving over 200 subjects) were randomised, double-blind and placebo-controlled. The majority of the study patients recruited have been in the USA under an Investigational New Drug (IND) Application, with the remainder having been recruited as part of studies undertaken in Australia.
Tissue Repair is in the final stages of completing its Phase II program, having recently completed Phase IIB clinical study data collection and statistical analysis across two indications: chronic wounds and aesthetic dermatology. The Company is planning to file end of study reports for its two Phase IIB trials with the FDA in 2021.
All Phase II trials have been undertaken employing FDA-approved protocols:
- Randomised: Trial subjects assigned to treatment or control groups using an element of chance to reduce selection and/or allocation bias.
- Double-blind: Neither the participants nor the administers know if they are being administered the placebo or trial treatment. Information which may influence the participants in the experiment is withheld.
- Placebo-controlled: Control group receive a non-effective “placebo” treatment specifically designed to have no real effect in order to benchmark again the treatment being trialled.
In a trial, patients can fall into two cohorts:
- Intention-To-Treat (ITT): Defined as patients that were randomised and recorded one observation. By way of example, if a patient withdrew in week 4 of a 12-week treatment period, they would still be included in the ITT group.
- Per Protocol (PP) or Completer Cohort: Defined as those patients that received the full course of treatment and the full dosage of TR-987, representing those patients that adhered to the approved trial protocol.
Program Overview
| Phase | Indication | Status | Year | Location | Patients | Design | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phase I/II | Chronic wounds (venous leg ulcers) | Completed | Australia | 6 | Open, observational |
|
|
| 18 | Double-blind, randomised, placebo controlled |
|
|||||
| Phase IIA | Chronic wounds (venous leg ulcers) | Completed | 2006 | Australia | 58 | Double-blind, randomised, placebo controlled |
|
| Phase IIA | Aesthetic (facial laser ablation) | Completed | 2007 | USA | Pilot – 12 Main – 26 |
Double-blind, randomised, placebo controlled |
|
| Phase IIB | Aesthetic (chest laser ablation) | Completed | 2020 | USA | 42 (across two studies with the same protocol) | Double-blind, randomised, placebo controlled (FDA approved) |
|
| Phase IIB | Chronic wounds (venous leg ulcers) | Completed | 2020 | USA/Australia | 82 | Double-blind, randomised, placebo controlled (FDA approved) |
|
Pivotal Clinical Studies
Ablative fractionated lasers have been increasingly utilised in recent years to improve the appearance of UV-induced photo-damage, skin wrinkles (rhytides) and scarring. Postoperative skin care is critical in promoting optimal wound healing after therapy, however there is currently no gold standard post procedural product.
Pivotal Clinical Studies
This study examined the efficacy of TR-987 in wound healing (epithelialisation) and improving skin quality following CO2 ablative laser treatment of the chest.
Pivotal Clinical Studies
The trial, which was done at a single site in San Diego, USA, and was randomised, double-blind, and placebo-controlled. The trial initially involved 22 patients and was later extended to include a further 20 patients (under two protocols which were materially identical). The data from both studies (n=42) was pooled and analysed. Two patients were lost to follow up (one each from the active and placebo groups) and an Intention-To-Treat (ITT) analysis was done on 42 patients together with a Modified Intention-To-Treat (MITT) analysis on the 40 patients who completed the trial.
The validated 3- and 9-point Fitzpatrick-Goldman Wrinkle and Elastosis Scale (respectively) was used to evaluate the effectiveness of the TR-987 0.1% gel in promoting post-procedure healing most notably as it affected skin quality of the underlying procedure as compared to control. Both test and control regimens promoted safe and effective healing of the chest skin after the procedure.
Pivotal Clinical Studies
Wrinkling
For the MITT group, 85% of responders achieved a wrinkling score of 1 or greater (i.e. 33% improvement) for the active group compared to the placebo group (where only 50% of responders achieved a wrinkling score of 1 or greater. The absolute difference of 35.0% is statistically significant (p = 0.041). The figure details the proportion of patients within each of the TR-987 and placebo groups who achieved a ≥1-point improvement in wrinkling scores between baseline and day 28 (Fitzpatrick-Goldman Classification).
Elastosis
For the MITT group, 75% of responders achieved an improvement score of 3 or greater in elastosis (i.e. 33% improvement) for the active group compared to the placebo group where only 35% of responders achieved the same level of improvement. The absolute difference of 40.0% is statistically significant (p = 0.011). The figure details the proportion of patients within each of the TR-987 and placebo groups who achieved a ≥3-point improvement in elastosis scores between baseline and day 28 (Fitzpatrick-Goldman Classification).

Pivotal Clinical Studies
The study investigators confirmed TR-987 to be an efficacious topical treatment following laser ablation in regard to improving skin quality as measured by elastosis and wrinkling.
Pivotal Clinical Studies: Phase IIA
The objectives of the study were to determine the efficacy of TR-987 in the promotion of repair of chronic venous insufficiency ulcers. The efficacy of two dosages of active ingredient, 0.1% and 1.0% GlucoprimeTM, were tested and assessed for safety and tolerance in ulcers of the lower limbs.
Pivotal Clinical Studies: Phase IIA
This was a 58 patient, Phase II, double-blind, placebo-controlled study with patients assigned to one of the three treatment groups on a randomised basis using a computer-generated allocation sequence. There were two active treatment arms (0.1% and 1.0% active ingredient respectively) in order to assess the dose-response effect of Glucoprime and a control arm of gel base with no active ingredient. The study was intended to provide a statistical assessment of the efficacy and safety of TR-987 in patients with chronic venous insufficiency ulcers of the leg. It was anticipated that the outcomes from this study would contribute towards the planning of a pivotal Phase III trial.
A subset of the Intention-To-Treat population, in which all subjects had measurements at both baseline and Day 85, was created and called the ‘Completer’ population for further analysis of efficacy (n = 14 in the high dose (1.0% TR-987) group and n = 15 in each of the low dose (0.1% TR-987) and placebo groups).
Pivotal Clinical Studies: Phase IIA
For the data analysis, non-parametric Wilcoxon rank sum tests with the Normal approximation were performed on the difference between placebo and each of the active treatment groups in the change in ulcer area from baseline to Day 85 for the Completer population. Statistically significant differences were found in the change in ulcer area from baseline to Day 85 for the high dose (1.0% TR-987) group compared with placebo (p = 0.022), and for the low dose (0.1% TR-987) group compared with placebo (p = 0.008).
Secondary analyses were carried out on the percent change from baseline to Day 85 for both populations using Wilcoxon ranked sum tests with the Normal approximation. There appeared to be a greater percent reduction in the low and high TR-987 dose groups than in placebo. While these apparent differences provided a positive indication of efficacy, they were not statistically significant, possibly due to the large variability in the data and to the relatively low sample sizes.
| Percent Change In Ulcer Area From Baseline | Intention-To-Treat Group (n=55) | Completer Group (n=44) (all subjects had measurements at both baseline and Day 85) |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Treatment | Median change in ulcer area | p-value | Median change in ulcer area | p-value |
| High Dose (1.0%) | -55.9% | 0.598 | -55.9% | 0.432 |
| Low Dose (0.1% | -59.0% | 0.301 | -66.7% | 0.115 |
| Placebo | -35.7% | -35.7% | ||
Pivotal Clinical Studies: Phase IIA
There was no evidence of any significant toxicity in any of the three treatment groups. Therefore, the safety profile for both the high and low dose formulations of TR-987 gel, as well as for the gel base, was considered to be acceptable.
The objectives of this study were to assess the time to heal within 12 weeks between chronic VLUs treated with TR 987 gel and Standard of Care (SoC) versus placebo gel and SoC.
This study was an 82 patient, multi-centre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study to evaluate the effectiveness of TR-987 gel on venous leg ulcers. It included a two-arm design with one group having received twice-weekly applications of 0.1% TR-987 in a gel base plus standard of care (SoC) for the first 4 weeks. The other group received twice-weekly applications of placebo gel base plus SoC for the same period. After 4 weeks, both groups received once weekly applications of their assigned treatment for the remaining 8 weeks of the trial.
Preliminary analysis of the trial has been conducted by Tissue Repair, with the final study report expected to be lodged with the FDA in 2021.
Statistical analysis was undertaken on both Intention-To-Treat (n=67) and Per Protocol (n=49) cohorts for the intended indication range of 2-12cm² and indicated that the primary objective of time to heal showed no difference between any of the groups. A key secondary objective of proportion of wounds healed, however demonstrated a positive signal of efficacy which is notable given wound closure is considered the gold standard FDA endpoint for wound healing.
Key findings from the preliminary analysis include the following:
- 20.6% adjusted improvement* in incidence of complete closure (p=0.12) for the Intention-To-Treat Group (n=67) for 2-12 cm² ulcers (logistic regression analysis)
- 27.37% improvement in incidence of complete closure (p=0.1029) for the Per Protocol group (n-49) 2-12 cm² ulcers (logistic regression analysis)
- Almost double the percentage wound area reduction in chronic venous leg ulcers 90.5% TR-987 vs 46.6% placebo for the per protocol group (p=0.035); 2-12cm² ulcers
*Adjusted difference based on logistic regression analysis, controlling for factors known to affect healing
- TR-987 per protocol group from the Phase IIB trial are those patients that completed the trial and received the full drug dosage over the 12-week period
- Intention-To-Treat group includes all patients randomised including all withdrawals
- A clinically meaningful difference is generally considered to be +10% difference of absolute closure
- TR-987 achieved 20.6% adjusted difference in incidence of complete closure vs adjusted incidence of complete closure for the current standard of care of 17%. Meaningful differences for the Intention-To-Treat group and Per Protocol groups are recorded
- Adjusted data is based on logistic regression (TR-987) and Cox regression (current standard of care) controlling for factors known to affect healing between the groups (e.g. base line ulcer size)


A typical example of a VLU wound healed with TR-987 2020 Phase IIB Venus Leg Ulcer trial n=67 (2-12cm²). 7.53cm² at screening (Heidelberg Repatriation Hospital Melbourne) Ulcer present for 208 weeks (4 years prior to enrolment) patient age was 72 with leg ulcers present from age 57
The ITT group includes all patients including early withdrawals while the PP group removes those patients who did not adhere to the protocol and were withdrawn prior to the 12-week treatment period and is considered a more meaningful measure of efficacy
NB: The protocol was undertaken during COVID-19 which caused a spike in patients lost to follow up. Ulcers were on average significantly larger in the Active group with 12 of the 36-patients having ulcers between 7-12 cm², This in comparison to placebo where only 2 of the 31 patients had ulcers in the 7-12cm² range.
The Phase IIB trial provided additional positive data in regard to the efficacy of TR-987 and confirmed a target indication wound size of 2-12cm² for the forthcoming Phase III trial.
When comparing the endpoint of average percentage of wound area reduction, the Phase IIB trial demonstrated a similar robust efficacy signal to the 2007 Phase IIA trial as shown below
- The 2007 Phase IIA trial treated severe wounds. Absolute mean wound area reduction (in mm²) showed statistically significant results between groups (p=0.08)
- 2007 phase IIA FDA VLU trial, mean percent wound area reduction for the completer group, low dose vs placebo. Note absolute mean wound area reduction showed statistically significant results [reduction of 1428mm² in low dose at day 85 vs 1084mm² in placebo (P=0.008)]
- 2020 Phase IIB FDA VLU trial mean percent wound area reduction for the 2-12cm² ulcer range per protocol group (the company’s target indication range
Early Clinical Studies
Glucoprime was studied in six patients with lower limb ulcers due to chronic deep venous insufficiency (CDVI) disease. Patients were selected on the basis of the long-standing nature of their ulcers and failure to respond satisfactorily to standard wound management. The test article was applied every 2-3 days for 4 weeks, and the ulcers were assessed weekly for response and signs of toxicity. The ulcer area was determined by planimetry.
No significant intolerances or toxicities were observed or reported in association with the use of the test article. A healing response was observed in all 6 patients, with an average reduction of 55% in wound surface area, measured over a 56-day period.
Early Clinical Studies
Phase I and II studies confirmed the ability of Glucoprime to stimulate and further initiate healing within chronic trophic ulcers.
The Phase IIA study sought to identify the optimal formulation (i.e. concentration of Glucoprime) of TR-987 gel that yielded the greatest efficacy.
Phase IIB was focused on further demonstrating the efficacy and safety of TR-987 against standard of care combined with a placebo gel.
The drug product has been well tolerated by patients across all clinical trials confirming a strong safety profile.
The completion of Phase II will be marked by an end of Phase II meeting with the FDA whereby Tissue Repair will share its findings from the Phase II patient trials and propose plans for a Phase III clinical study.
The efficacy of Glucoprime was studied in a single-centre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial in 18 patients with CDVI ulcers that had become refractory to standard wound management therapies. Glucoprime was compared to another form of glucan (Glucodine) with a lower molecular weight range and a smaller proportion of (1->6)-β-glucan side-branching, and to the placebo (control). Patients were randomly assigned to the three treatment groups (two active groups and one placebo control group), with 6 patients per group. Treatment was 3 times weekly for 4 weeks. No intolerances or toxicities were observed or reported in association with the use of either of the active test articles or placebo control. Efficacy was assessed by planimetry, measuring the surface area of the wound. The primary efficacy parameter was the improvement in ulcer surface area from baseline (visit 1) to the end of the trial (visit 6). The mean rates of improvement over 4 weeks were as indicated in the table. Ulcer healing was improved in patients in the Glucoprime group compared to placebo, and the results of this study were used to plan further studies using a larger number of patients over a longer treatment period.
| Summary Mean Rates Of Ulcer Improvement Over 4 Weeks | |
|---|---|
| Treatment | Percent Reduction In Wound Surface Area After 4 Weeks Of Treatment (a minus value indicates wound worsening) |
| Glucoprime (high molecular weight API) | 36.7% |
| Glucodine (low molecular weight API) | -17.3% |
| Placebo (control) | 4.4% |

Early Clinical Studies
The study evaluated the safety and efficacy of two concentrations of TR-987 (low and high Glucoprime dosages) compared to placebo (gel base), in promoting wound healing on the lower eyelid skin of 26 subjects undergoing fractionated CO2 laser skin resurfacing for cosmetic purposes (wrinkle reduction). Overall, when compared to placebo, treatment with TR-987 (high Glucoprime dosage) or TR-987 (low Glucoprime dosage) was safe and well tolerated.
The comparison of each TR-987 arm to placebo with respect to the primary endpoint (mean time to complete wound closure / epithelialisation) showed positive results when considering the full subject dataset from all treatment combinations. Specifically, the efficacy outcome of time to complete wound closure was 20-30% shorter for TR-987 at 1.0% and 0.1% (13.1 days and 10.9 days, respectively) compared to placebo (16.3 days; p = 0.0062 and 0.0331, respectively).
In vivo studies looking at incisional wounds in mice, rats, guinea pigs and mini pigs have all confirmed clinical efficacy of Glucoprime (the Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient (API) of TR-987) and its precursors.
The primary effects of the Glucoprime therapy were enhanced migration of macrophages and neutrophils into the wound space, followed by earlier onset of all aspects of the healing cascade.
Leibovich SJ, Danon D. Promotion of wound repair in mice by application of glucan. J. Reticuloendothel. Soc. 27, 1-11 (1980)
Clinical Pathway
Tissue Repair has commenced preparatory work for the TR-987 Phase III clinical trial on venous leg ulcers and is expecting the study to take an estimated 36 months to complete, assuming no delays in patient recruitment, or onerous FDA requests in relation to the characterisation of the active ingredient, Glucoprime.
Clinical Pathway
The Phase III clinical trial is being designed in accordance with FDA requirements to allow Tissue Repair to pursue regulatory approval in the USA. If successful, TR-987 may be the only topical drug approved for wound care in the USA since 1997 and as such, may represent a valuable asset with a significant market opportunity.
The key work streams required to successfully commence, and complete Phase III trials include:
| A | Analytical development and product manufacture |
|
| B | Regulatory |
|
| C | Phase III trial |
|